Eyewear Info
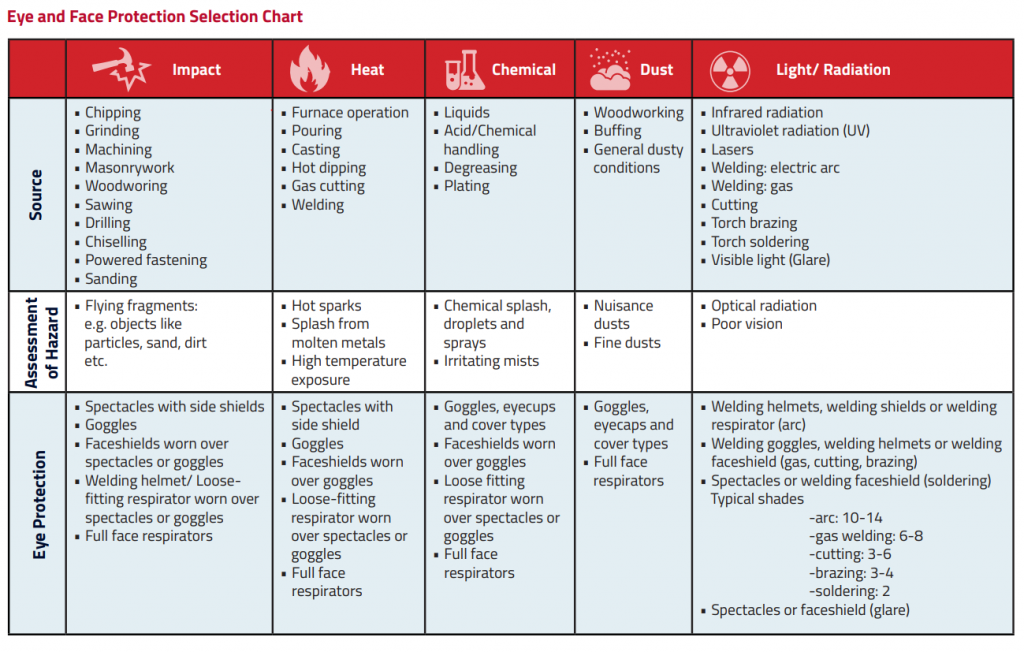
Protectors should be mandatory where there is a reasonable probability of an eye or face injury that can be reduced or prevented with the use of protectors. A hazard assessment should be conducted to decide the risk of exposure in order to select the appropriate protectors needed. The safety officer or other responsible parties should pay attention to the different types of hazards and identify the sources of the hazards as stated below. After evaluating the information gathered, suitable protectors should be selected and used.
2.1 Minimum Requirements
Meets International Safety Standards, e.g. ANSI Z87.1-2015/2010, SS473:2011, EN166:2001, GB, JIS, AAS, AS/NZS 1337.6
2.2 Optical Quality

2.3 High Impact Rating
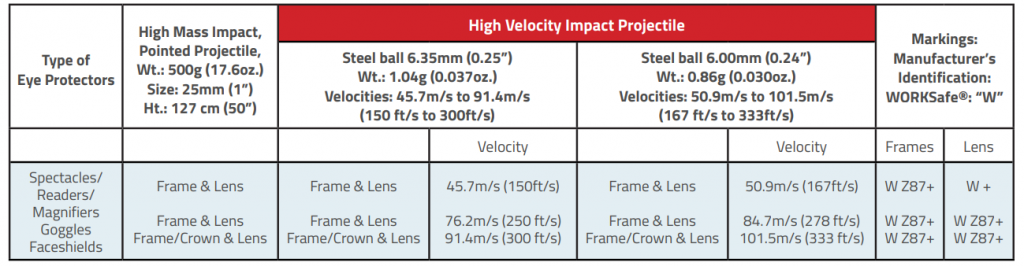
2.3.1 American Standards ANSI/ISEA Z87.1
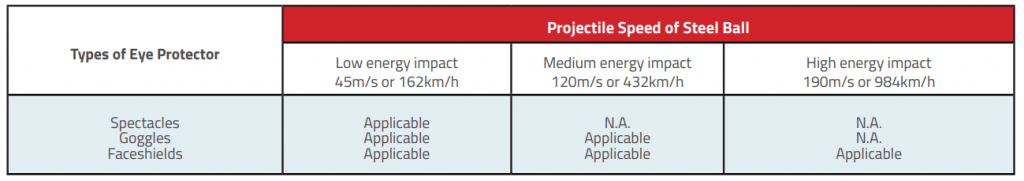
2.3.2 EN166
2.4 Lens Materials
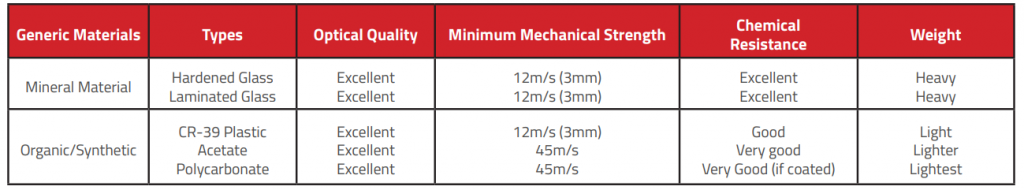
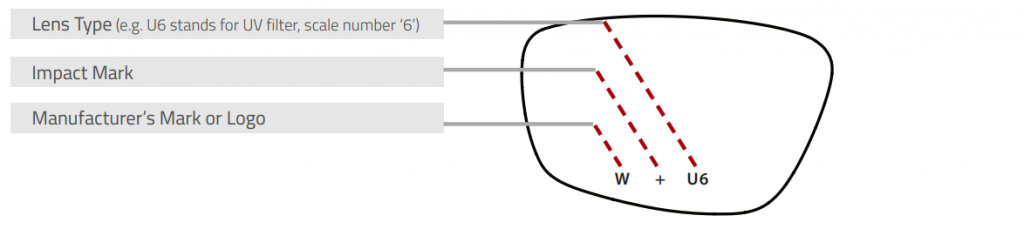
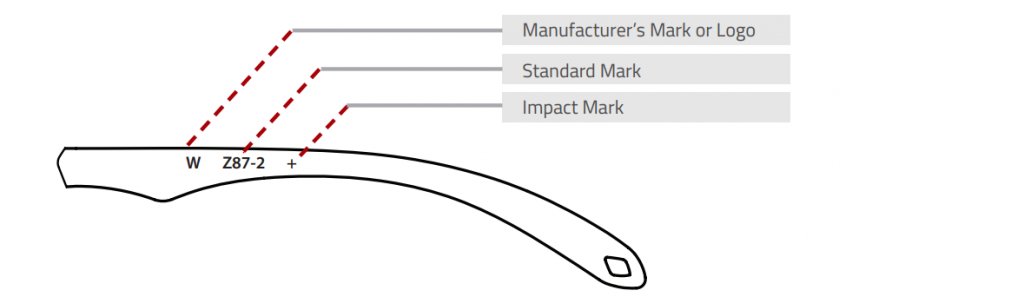
3.1 ANSI/ISEA Z87.1 Marking Requirements
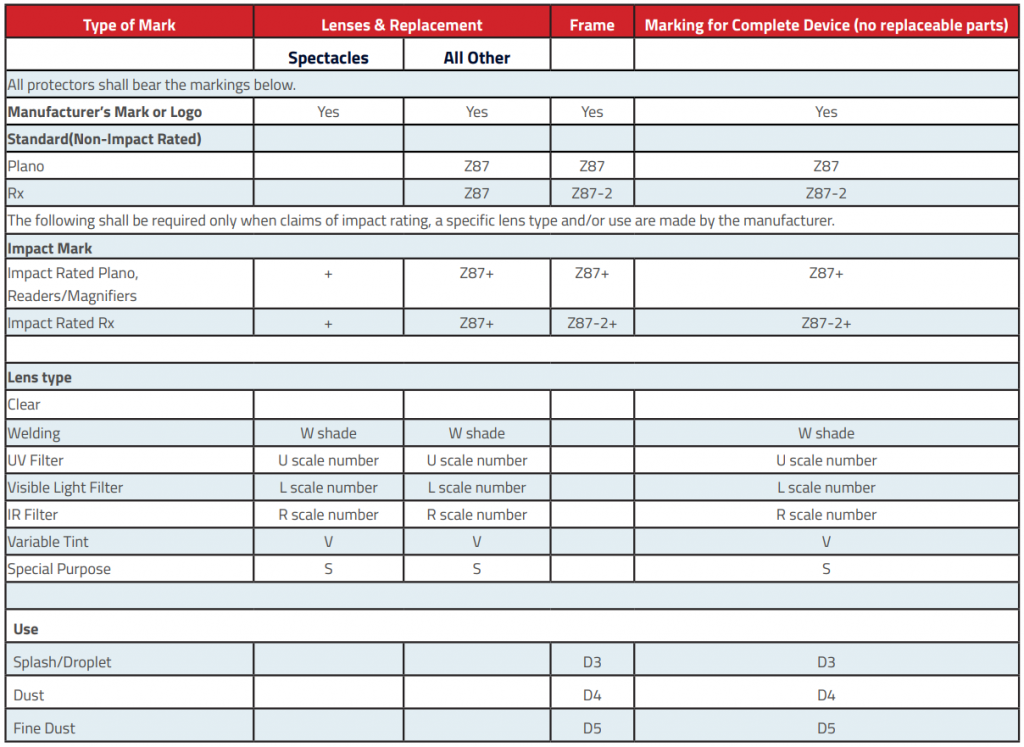
3.2 ANSI/ISEA Z87.1 Marking Sequence
Markings can follow a top to bottom sequence or a left to right sequence. DISCLAIMER: The information below is provided to demonstrate examples of resulting product markings compliant with ANSI/ISEA Z87.1-2015. Such information is not meant to be all-inclusive and is provided for illustrative purposes only.
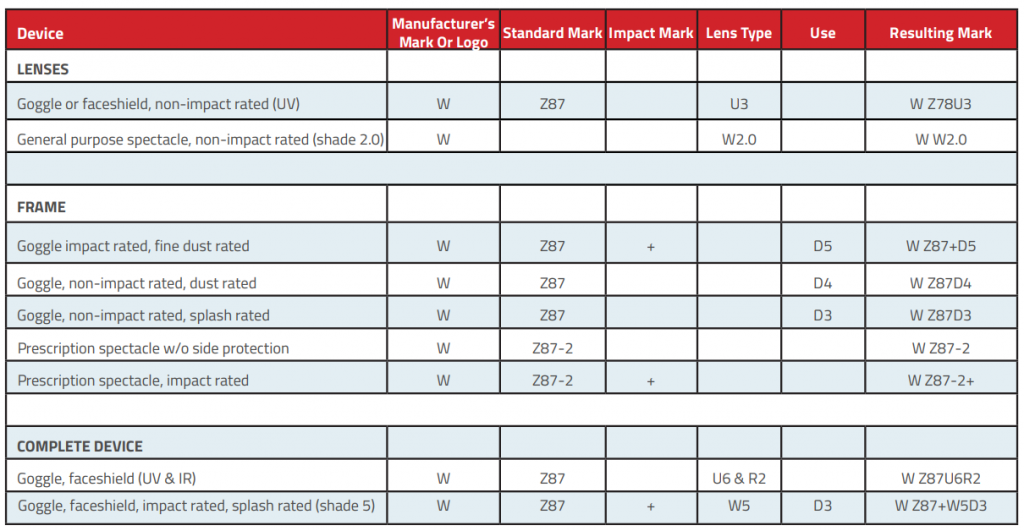
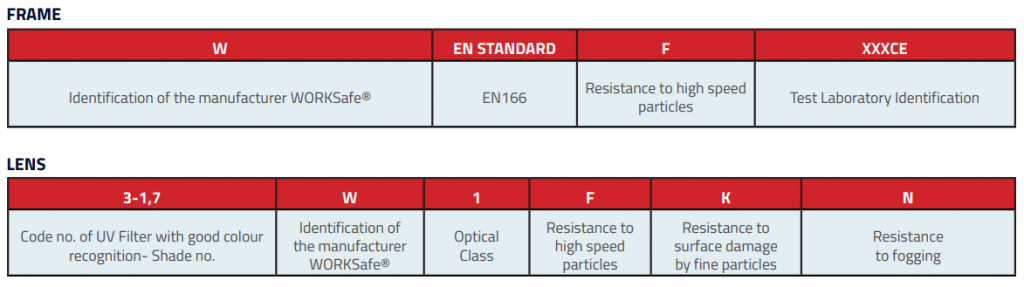
3.3 EN166
3.4 Wearers’ comfort & acceptance in accordance with SS473 standards
- Lightweight for prolonged wearing and use
- Good fitting with temple length adjustment
- Good fitting for different nose bridges with temple inclination height adjustment
- Eye and bridge sizes suitable for Western or Asian people
- Pressure points reduced by soft, tri-flex or dual density anti-slip temples
- Well ventilated or with anti-fog features
- Polycarbonate lens must have durable anti-scratch and anti-fog coating for clarity
- Material should withstand tropical climate, high humidity and temperature
3.5 Additional consideration for goggles in accordance with SS473 standards
- Wide vision for panoramic view
- Good face sealing for better protection and comfort
- Wide headband for increased comfort
- Able to wear over prescription spectacles
- Choice of lens material such as acetate, propionate or polycarbonate
New ANSI Z87.1-2015 allows the use of a steel ball of diameter 6mm (0.24”), travelling at 50.9m/s (167 ft/s) or a steel ball with diameter 6.35mm (0.25”) travelling at 45.7m/s (150 ft/s) when conducting the high velocity impact test on the complete devices.
Safety Prescription (SRX) Lens Material Qualification
Representative SRX lens must be tested to resist high velocity impact using steel ball of either diameter 6mm and 6.35mm as specified in Section 2.3.1.
Safety Prescription (SRX) Lens Mounting Qualification
Complete SRX eyewear with representative test lens and retention system shall be capable of resisting high velocity impact using steel ball of either diameter 6mm and 6.35mm as defined in Section 2.3.1.
Special Purpose Filters
Special purpose filters, both tinted and extra dark, marked “S”, may or may not comply to requirements for welding, UV and visible light filters, but shall comply with the transmittance requirements for special purpose lenses.
Visible Light Filters
Protectors marked L1.3 to L3 must meet transmittance requirements of traffic signal recognition and UV transmittance of ANSI Z80.3-2010, American National Standard for Ophthalmics – Nonprescription Sunglasses and Fashion Eyewear Requirements. While protectors marked L4 to L10 are too dark to be used for driving, they shall meet UV transmittance requirements of ANSI Z80.3-2010.
Transmittance of Non-Lens Components
If a spectacle claims to meet the transmittance requirements of welding, UV and infrared filter lenses, the side shields of the spectacles shall be tested to the maximum scale number of the lens with which they will be fitted. Wraparound lenses which have the side protection as part of the lenses will be subjected to the same testing.
Angular Dependence of Luminous Transmittance
Requirements for angular dependence of luminous transmittance for welding filters have also been added to address visual effect that welders can find both dangerous and disturbing.
In ANSI Z87.1-2015, the tests for droplet and splash, dust, and fine dust hazards are intended to determine the capability of the protector to keep liquid splashes or sprays, large dust and fine dust particles, from reaching the wearer’s eyes. Eyewear that pass each test are marked additionally with D3, D4, and D5 respectively. (Refer to table 3.5.1) Add Accordion Item
1. Minimum Lens Thickness of SRX Lens
SRX eyewear must be fitted with impact rated SRX lens with a minimum thickness of 2mm (0.08”)
2. SRX Optical Requirements – Refractive Power, Astigmatism, Prism and Prism Imbalance for RX Protectors and Magnifiers
SRX lens must be tested according to and comply with the tolerance on refractive power, astigmatism, prism and prism imbalance as stated in ANSI Z80.1-2010, American National Standard for Ophthalmics – Prescription Ophthalmic Lenses Recommendations.
3. SRX Lens Mounting Qualification
Complete SRX eyewear with representative test lens and retention system shall be capable of resisting high mass and high velocity impact. A new lens retention test is required of prescription safety laboratories fabricating impact rated SRX eyewear to determine their ability to consistently produce lenses that will be retained in the various frame types they choose to sell.
4. SRX Lens Material Qualification
Representative SRX lens must be tested to resist high velocity impact using a steel ball of diameter 6mm (0.24”) travelling at 50.9m/s (167 ft/s) or a steel ball with diameter 6.35mm (0.25”) travelling at 45.7m/s (150 ft/s).
5. SRX Lens Carrier (RX Insert)/SRX Eyewear with Lift Fronts
The complete device with prescription lenses in +5.0 and -5.0 diopters fitted in the carrier, behind the plano eyewear shall be tested. RX lens carrier used behind plano protectors shall be marked with the manufacturer’s mark or logo but not any other Z87 markings. Complete devices with SRX eyewear and lift fronts shall be tested with the lift front in the “up” position.
6. SRX Side Shield Attachment
SRX eyewear must be equipped with side shields that can be securely or permanently attached to pass the side impact test.
The American National Standards Institute (ANSI) has approved and issued the new ANSI/ISEA Z87.1-2015 American National Standard for Occupational and Educational Eye and Face Protection (ANSI Z87.1-2015). This standard went into effect May 28, 2015, and updates the 2010 version. While the scope of the standard remains mostly unchanged, there are a number of modifications that have significant impact. The following outlines these changes and how they impact eye protection and the methods companies use to select safety products.
Important Changes
ANSI Z87.1-2015 continues to focus on product performance and reflects the need to streamline testing methods to harmonize with global standards to allow new and innovative designs to protect against hazards, meet end-users needs and workplace regulations. This consists of acceptance of protectors known as “magnifiers” and “readers” that have lenses, or portion of lenses that have magnification properties. The new Z87.1-2015 standard fine-tunes the hazard-based structure of choosing protectors, a concept first introduced in 2010. In the revised standard, additional emphasis has been placed on enabling users to select protectors suitable for their working environment and providing end-users with information to facilitate the selection process.
Optical Requirements of Refractive Powers
ANSI Z87.1-2015 specifies that the telescope and observer shall be qualified by resolving pattern 40 of the test pattern instead of pattern 20. The revised standard states that the average refractive power of lenses with astigmatism is used instead of each meridian.
Physical Requirements of Drop Ball Impact Resistance
ANSI Z87.1-2015 elaborates on the specifications of testing apparatus used in the drop ball test. The projectile will be dropped from a height of 127cm (50”) through a loose fitting guide tube with a smooth internal diameter ending 10cm (4”) above the point of contact. The revised standard eliminates the need to perform drop ball testing for a protector that is first tested to and meet the requirements of impact resistance.
According to clause 5.3 of the SS473: Part 2:2011 Singapore Standard, eye protectors (plano and prescription eye protectors) must comply and be marked in accordance with any of the following standards or their equivalent: ISO, EN (Europe), ANSI (USA), CSA (Canada), AS/NZ (Australia/New Zealand) and JIS (Japan). All WORKSafe® eyewear comply with SS473 as well as ANSI/ISEA Z87.1 standards, and, if indicated, EN166 standards.
Follow these care instructions for long-lasting comfort and protection!
1. To avoid breaking or bending your spectacle frame, handle your glasses with both hands. Pull both ear rails simultaneously when putting on or taking off your glasses.
2. When not in use, store your glasses in a case like the WORKSafe® SRX
3. If you haven’t got a case, be sure to place your WORKSafe® safety eyewear upright, so the lenses don’t get scratched or scuffed.
4. Clean your glasses regularly with microfiber cloths or with WORKSafe® Kleanlens® solution; or by washing them with mild soap and water.
5. Avoid exposing your glasses to extreme temperatures, under direct sunlight, or during your bath. Smoke, heat and steam can damage the lens coating